In the Forex market, currency pairs are the foundation of all trading activities. A currency pair is a quotation of two different currencies, with the value of one currency being quoted against the other. The first currency in the pair is known as the base currency, while the second is the quote currency. This relationship reflects how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. Understanding currency pairs is crucial for anyone looking to engage in Forex trading, as it forms the basis of all buying and selling activities in this global market.
Currency pairs are categorized into three main types: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs. Major pairs involve the most traded currencies globally and typically include the US dollar, such as EUR/USD or USD/JPY. Minor pairs, also known as crosses, do not involve the US dollar and often include currencies like the euro and the British pound. Exotic pairs consist of one major currency paired with a currency from an emerging or smaller economy, such as USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira). Understanding these distinctions and how they operate within the Forex market can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to make informed decisions and manage risks effectively.
Table of Contents
What Are Currency Pairs in Forex?
Currency pairs in the Forex market represent the quotation and pricing structure of the currencies being traded. A currency pair consists of two currencies: the base currency and the quote currency. The exchange rate tells you how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, the euro (EUR) is the base currency and the US dollar (USD) is the quote currency. If the exchange rate for EUR/USD is 1.20, it means one euro is equivalent to 1.20 US dollars.
Forex trading involves buying one currency while simultaneously selling another, which is why currencies are always traded in pairs. This structure allows traders to speculate on the price movements of one currency relative to another, capitalizing on fluctuations in exchange rates driven by various economic, political, and market factors.
How Do Currency Pairs Work?
Currency pairs operate on the principle of relative value. The value of a currency pair is influenced by the economic health of the respective countries, interest rates, inflation, political stability, and other macroeconomic factors. When traders buy a currency pair, they are buying the base currency and selling the quote currency. Conversely, when they sell a currency pair, they are selling the base currency and buying the quote currency.
For instance, if a trader believes that the euro will strengthen against the US dollar, they might buy the EUR/USD pair. If the exchange rate rises, they can sell the pair at a higher rate, thus making a profit. Conversely, if they expect the euro to weaken against the dollar, they would sell the EUR/USD pair
What Are Major Currency Pairs?
Major currency pairs in the Forex market are those that are most frequently traded and include the US dollar paired with other significant global currencies. These pairs are known for their high liquidity, tight spreads, and substantial trading volumes, making them attractive to traders. The most commonly recognized major pairs include EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, and USD/CHF. These pairs represent the largest economies and are heavily influenced by economic indicators, monetary policies, and geopolitical events from their respective countries.
The EUR/USD pair, for instance, represents the Eurozone and the United States, which are two of the world’s largest economies. This pair is the most traded, accounting for a significant portion of daily Forex transactions. The USD/JPY pair, also known as “The Ninja,” involves the US dollar and the Japanese yen and is popular due to Japan’s role as a major financial hub and the yen’s status as a carry trade currency. The GBP/USD pair, often referred to as “Cable,” is influenced by the economic activities and policies in the UK and the US, including Brexit-related developments. Lastly, the USD/CHF pair, which involves the US dollar and the Swiss franc, is known for its stability and is often seen as a safe-haven pair during times of market uncertainty.
What Are Minor Currency Pairs?
Minor currency pairs, also known as cross-currency pairs, do not include the US dollar but involve other major currencies such as the euro, pound sterling, or yen. These pairs are less liquid than major pairs and generally have wider spreads, but they still offer significant trading opportunities, particularly for those looking to diversify their portfolios.
Examples of minor currency pairs include EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY, and EUR/AUD. The EUR/GBP pair, which represents the euro against the British pound, is influenced by economic conditions in the Eurozone and the United Kingdom. GBP/JPY involves the British pound and the Japanese yen, and it is known for its volatility and significant price swings, influenced by economic data and policy decisions from both the UK and Japan. The EUR/AUD pair, which includes the euro and the Australian dollar, is affected by the economic health and trade relationships of the Eurozone and Australia.
What Are Exotic Currency Pairs?
Exotic currency pairs consist of one major currency paired with the currency of an emerging or smaller economy. These pairs are characterized by lower liquidity, higher volatility, and wider spreads, making them riskier and often more expensive to trade. However, they can offer significant profit opportunities due to their large price movements.
Examples of exotic currency pairs include USD/TRY (US dollar/Turkish lira), USD/ZAR (US dollar/South African rand), and EUR/MXN (euro/Mexican peso). These pairs are influenced by the economic and political conditions of the emerging markets they represent. For instance, USD/TRY is impacted by Turkey’s economic policies, inflation rates, and political stability, while USD/ZAR reflects the economic health and commodity exports of South Africa. Traders interested in exotic pairs must stay informed about the specific factors affecting these currencies to manage the associated risks effectively
How to Read Forex Quotes?
Understanding Forex quotes is essential for any trader in the Forex market. A Forex quote is the price of one currency in terms of another currency and always involves two currencies: the base currency and the quote currency. The base currency appears first in the pair, and the quote currency comes second. For example, in the EUR/USD pair, EUR is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency.
Forex quotes are displayed with two prices: the bid price and the ask price. The bid price is the price at which you can sell the base currency, while the ask price is the price at which you can buy the base currency. The difference between these two prices is called the spread, which represents the broker’s profit margin. For instance, if the EUR/USD quote is 1.1200/1.1205, you can sell one euro for 1.1200 US dollars (bid price) and buy one euro for 1.1205 US dollars (ask price). The spread in this example is 0.0005, or 5 pips.
What is the Bid and Ask Price in Forex?
The bid price and the ask price are crucial components of a Forex quote. The bid price is the maximum price that a buyer is willing to pay for a currency. Conversely, the ask price is the minimum price that a seller is willing to accept for a currency. This two-way price quotation ensures that there is always a buyer and a seller for a given currency pair.
The spread, which is the difference between the bid and ask prices, is a measure of the market’s liquidity and the broker’s profit. A smaller spread indicates a more liquid market, while a larger spread indicates less liquidity. For example, in the quote USD/JPY 110.50/110.55, the bid price is 110.50, and the ask price is 110.55, resulting in a spread of 5 pips..
How is the Spread Calculated in Forex Trading?
The spread is calculated as the difference between the bid price and the ask price. It is measured in pips, which stands for “percentage in point,” and is the smallest price move in a Forex quote. For most currency pairs, one pip equals 0.0001, except for pairs involving the Japanese yen, where one pip equals 0.01.
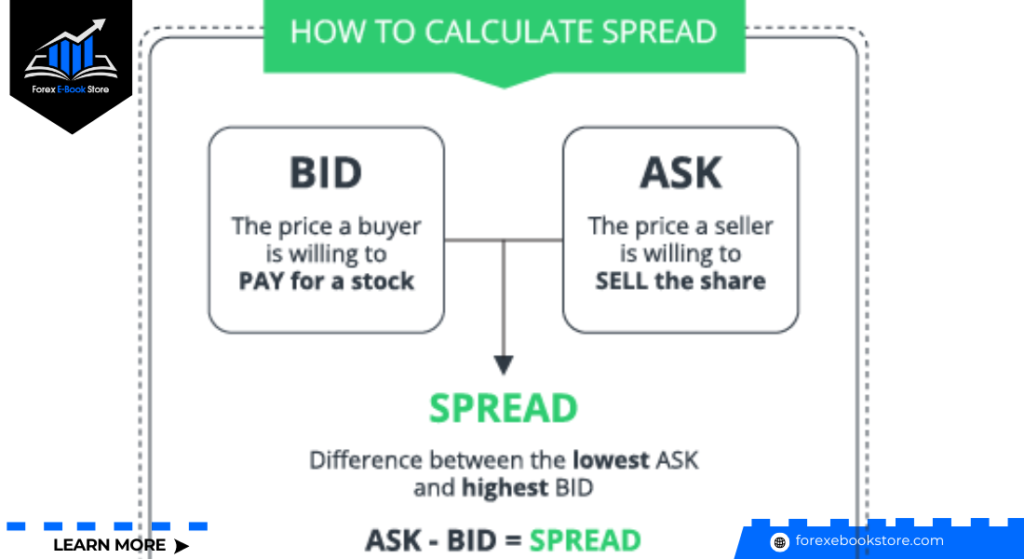
For example, if the EUR/USD pair is quoted at 1.1200/1.1205, the spread is 0.0005, or 5 pips. This spread is the cost of the trade and represents the broker’s compensation for facilitating the transaction. Lower spreads are preferable for traders as they reduce the cost of trading, especially for those who trade frequently or in large volumes.
What Factors Affect Currency Pair Prices?
Understanding the factors that affect currency pair prices is crucial for Forex traders. These factors can be broadly categorized into fundamental, technical, and geopolitical influences.
Fundamental Factors: Economic indicators play a significant role in determining currency pair prices. Key indicators include GDP growth, inflation rates, employment data, and interest rates. For example, higher GDP growth often strengthens a currency, while higher inflation can weaken it. Central banks, like the Federal Reserve or the European Central Bank, influence currency values through monetary policies such as interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing. When central banks raise interest rates, it often attracts foreign investment, increasing the currency’s value.
Geopolitical Events: Political stability and geopolitical events also significantly impact currency pair prices. Political instability, wars, and conflicts can lead to uncertainty and volatility in the Forex market. For instance, the Brexit vote caused substantial fluctuations in the value of the British pound. During times of uncertainty, investors often flock to safe-haven currencies like the US dollar or the Japanese yen.
Technical Factors: Market sentiment and technical analysis are crucial in influencing currency pair prices. Traders’ perceptions and attitudes towards a currency can drive its demand and value. Technical analysis involves studying historical price patterns and using indicators to predict future movements, helping traders make informed decisions. Order flow, which represents the buying and selling activities in the market, also impacts currency values. High demand can drive up a currency’s price, while excess supply can drive it down.
How to Choose Which Currency Pairs to Trade?
Choosing the right currency pairs to trade involves understanding market conditions, personal trading styles, and the specific characteristics of the currency pairs.
Liquidity and Volatility: Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY, are known for their high liquidity and tighter spreads, making them ideal for traders who prefer stable and predictable markets. These pairs are heavily traded, offering ample opportunities for both short-term and long-term trades. On the other hand, exotic pairs like USD/TRY or EUR/ZAR are less liquid and more volatile, which can provide higher profit opportunities but also carry greater risk.
Economic Indicators: Traders often choose currency pairs based on their familiarity with the economic indicators affecting those currencies. For example, if you are well-versed in European and US economic data, trading EUR/USD might be advantageous. Staying informed about economic releases, central bank announcements, and geopolitical events can help in making informed trading decisions.
Correlation: Understanding the correlation between different currency pairs can help in managing risk. Positive correlation means pairs move in the same direction, while negative correlation means they move in opposite directions. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD often have a positive correlation. By diversifying trades across correlated and uncorrelated pairs, traders can balance their portfolios and reduce risk exposure.
What Are Commodity Currency Pairs?
Commodity currency pairs involve currencies from countries that are major exporters of commodities, such as oil, gold, or agricultural products. These pairs include currencies like the Australian dollar (AUD), Canadian dollar (CAD), and New Zealand dollar (NZD).
AUD/USD: The Australian dollar is closely tied to commodities like iron ore and coal. Fluctuations in commodity prices can significantly impact the AUD/USD pair. For instance, rising commodity prices can strengthen the Australian dollar as it boosts the country’s export revenues.
USD/CAD: The Canadian dollar is heavily influenced by oil prices since Canada is one of the largest oil exporters. When oil prices rise, the CAD typically strengthens against the USD, making the USD/CAD pair highly sensitive to changes in the oil market.
NZD/USD: The New Zealand dollar is affected by agricultural commodity prices, including dairy and meat products. Economic conditions in major trading partners, like China, also play a significant role in the NZD’s value
What is Currency Pair Correlation?
Currency pair correlation in Forex refers to the relationship between the movements of two currency pairs. It quantifies the degree to which the pairs move in the same or opposite directions. A positive correlation means that the pairs move in the same direction, while a negative correlation means they move in opposite directions. For example, EUR/USD and GBP/USD often have a positive correlation, whereas EUR/USD and USD/CHF typically have a negative correlation.

Understanding currency correlation is crucial for Forex traders as it helps in risk management and portfolio diversification. By recognizing correlated pairs, traders can avoid placing multiple trades that might expose them to the same market risks. Conversely, identifying negatively correlated pairs can help in hedging positions to mitigate potential losses.
How to Use Technical Analysis on Currency Pairs?
Technical analysis involves studying past price movements and patterns to predict future price behavior. In Forex trading, this analysis is primarily conducted using charts and technical indicators. Common chart types include line charts, bar charts, and candlestick charts, each offering different insights into price trends and patterns.
Key technical indicators used in Forex trading include moving averages, which help identify the direction of the trend; the Relative Strength Index (RSI), which measures the speed and change of price movements; and Bollinger Bands, which provide a range within which a currency pair is expected to trade. By analyzing these indicators, traders can identify potential entry and exit points for their trades.
What Are the Risks of Trading Exotic Currency Pairs?
Exotic currency pairs consist of one major currency paired with a currency from an emerging or smaller economy. These pairs are known for their high volatility and lower liquidity compared to major and minor pairs. Examples include USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira) and USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand).
The primary risk of trading exotic pairs is their volatility, which can lead to large price swings and significant potential losses. Additionally, the wider spreads associated with these pairs increase the cost of trading. Economic and political instability in the countries of the exotic currencies can also lead to unpredictable market movements, making these trades riskier. However, for traders who can manage these risks effectively, exotic pairs can offer substantial profit opportunities due to their high volatility.
How Do Economic Indicators Influence Currency Pairs?
Economic indicators are critical in shaping the movements of currency pairs in the Forex market. These indicators reflect the economic health of a country and influence investor sentiment, impacting currency values. Key economic indicators include GDP growth, inflation rates, employment data, and interest rates.
GDP Growth: Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced within a country. Higher GDP growth signals a strong economy, often leading to an appreciation of the country’s currency. For example, if the UK’s GDP growth surpasses expectations while the US GDP growth falls short, the GBP/USD exchange rate is likely to rise.
Inflation Rates: Inflation refers to the overall increase in prices of goods and services. Central banks use interest rate adjustments to control inflation. Higher inflation generally leads to higher interest rates, attracting foreign investment and strengthening the currency. Conversely, low inflation might prompt central banks to lower interest rates, weakening the currency.
What Are Cross Currency Pairs?
Cross-currency pairs, also known as cross rates, are currency pairs that do not involve the US dollar. These pairs represent direct trading between two currencies without the need to convert to USD first. Examples of cross currency pairs include EUR/GBP, GBP/JPY, and EUR/AUD.
EUR/GBP: This pair represents the euro against the British pound. It is influenced by the economic conditions and political events in both the Eurozone and the UK. Brexit negotiations, for instance, have had significant impacts on the EUR/GBP exchange rate.
GBP/JPY: This pair involves the British pound and the Japanese yen. Known for its volatility, GBP/JPY is influenced by economic data from the UK and Japan, as well as global risk sentiment. During times of market uncertainty, the yen, being a safe-haven currency, often strengthens.
What Role Does Liquidity Play in Currency Pair Trading?
Liquidity refers to the ease with which a currency can be bought or sold in the Forex market without affecting its price. High liquidity means there are numerous buyers and sellers, leading to tighter spreads and less price volatility. Major currency pairs, such as EUR/USD and USD/JPY, are known for their high liquidity.
High Liquidity Benefits: High liquidity ensures that traders can enter and exit positions with minimal slippage, making it easier to execute large trades. It also results in tighter spreads, reducing trading costs. This makes major pairs attractive for both short-term and long-term trading strategies.
Low Liquidity Risks: Currency pairs with lower liquidity, such as exotic pairs, often have wider spreads and are more susceptible to price manipulation and volatility. This can result in larger price swings and higher trading costs, posing greater risks for traders. Therefore, understanding liquidity is crucial for managing risk and making informed trading decisions.
What Are Direct and Indirect Currency Quotes?
In Forex trading, understanding the difference between direct and indirect currency quotes is crucial for making informed trading decisions.

Direct Quotes: A direct quote shows how much of the domestic currency is needed to purchase one unit of the foreign currency. For example, in the United States, if the EUR/USD quote is 1.20, it means one euro costs 1.20 US dollars. Here, the domestic currency (USD) is the quote currency, and the foreign currency (EUR) is the base currency. Direct quotes are more intuitive and easier to understand for traders as they simplify the process of converting currencies.
Indirect Quotes: An indirect quote, on the other hand, expresses the amount of foreign currency required to purchase one unit of the domestic currency. For example, if the indirect quote for USD/JPY is 110, it means one US dollar is worth 110 Japanese yen. This format is less common and can be more complex because it involves additional calculations to understand the value of the domestic currency in terms of the foreign currency.
What Are the Best Practices for Trading Currency Pairs?
Trading currency pairs effectively requires a well-structured approach and adherence to best practices. Here are some key strategies:
Education and Research: Before diving into Forex trading, it is essential to understand the market fundamentals, including how currency pairs work, the factors that influence exchange rates, and the different types of analysis (technical and fundamental). Continuous learning and staying updated with market news and economic indicators are crucial.
Choosing the Right Broker: Selecting a reliable and reputable Forex broker is important. Look for brokers that offer competitive spreads, reliable execution speeds, and robust trading platforms. Ensure the broker is regulated by a recognized authority to protect your investments.
Developing a Trading Plan: A well-defined trading plan is crucial for consistency and discipline. This plan should include your trading goals, risk tolerance, entry and exit strategies, and criteria for selecting trades. Stick to your plan and avoid making impulsive decisions based on market emotions.
Risk Management: Implementing proper risk management techniques is essential to protect your capital. This includes using stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, diversifying your trades, and not risking more than a small percentage of your capital on a single trade. Understanding and managing leverage is also critical, as it can amplify both gains and losses.
How to Manage Risk When Trading Currency Pairs?
Effective risk management is crucial for long-term success in Forex trading. Here are some strategies to help manage risk:
Use Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order is a pre-determined point at which you will exit a trade to prevent further losses. This tool helps limit your downside risk and protect your capital. Setting a stop-loss level based on technical analysis or a fixed percentage of your trading account is a common practice.
Diversification: Spread your investments across different currency pairs to reduce exposure to any single pair’s volatility. This strategy helps mitigate risk by not putting all your capital into one trade, which could result in significant losses if the market moves against you.
Leverage Management: While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases the risk of significant losses. Use leverage cautiously and understand its impact on your trading account. It is advisable to use lower leverage ratios to minimize risk, especially for beginners
Conclusion.
Understanding currency pairs is fundamental to navigating the world of Forex trading. By grasping how major, minor, and exotic pairs function, you equip yourself with the knowledge needed to make informed trading decisions. As you deepen your understanding of currency pairs, it’s essential to revisit the basics—like What is Forex?—to ensure a solid foundation in this dynamic market. Both concepts are intertwined, as mastering currency pairs enhances your overall Forex trading strategy.












