What is a Spread?, In the Forex market, the spread is the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell a currency pair) and the ask price (the price at which you can buy a currency pair). Essentially, it represents the cost of trading and is a primary source of income for brokers. For instance, if the EUR/USD bid price is 1.1000 and the ask price is 1.1005, the spread is 5 pips. Understanding the spread is crucial for traders because it directly affects the profitability of their trades.
The spread can vary depending on several factors, including market conditions, the currency pair being traded, and the broker’s pricing model. During periods of high liquidity, such as when major trading sessions overlap, spreads tend to be narrower. Conversely, spreads can widen during periods of high volatility, such as during significant economic news releases. By understanding how spreads work, traders can better manage their costs and make more informed trading decisions.
Table of Contents
How is the Spread Calculated in Forex?
The spread in Forex trading is calculated as the difference between the bid price (the price at which you can sell a currency pair) and the asking price (the price at which you can buy a currency pair). This difference is measured in pips, the smallest unit of price movement in Forex trading. For most currency pairs, a pip is equivalent to 0.0001, while for pairs involving the Japanese yen, a pip is 0.01.
For example, if the EUR/USD pair has a bid price of 1.2000 and an ask price of 1.2005, the spread would be 5 pips (1.2005 – 1.2000 = 0.0005). Calculating the spread is essential because it represents the primary cost of trading and can significantly impact a trader’s profitability. Traders prefer narrower spreads as they reduce trading costs and make it easier to enter and exit positions at desired prices.
What are the Different Types of Forex Spreads?
Forex spreads can be broadly categorized into two types: fixed spreads and variable (or floating) spreads.
Fixed Spreads: Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. Brokers offering fixed spreads provide traders with stability and predictability, as the spread does not change even during periods of high volatility. However, fixed spreads are often wider than variable spreads to account for the broker’s risk. Fixed spreads are particularly beneficial for novice traders who need consistency in their trading costs.
Variable Spreads: Variable spreads fluctuate with market conditions, such as liquidity and volatility. During periods of high liquidity, such as when major trading sessions overlap, spreads tend to be narrower. Conversely, during high volatility or low liquidity periods, spreads can widen. Experienced traders often prefer variable spreads because they benefit from lower trading costs during stable market conditions. However, they must be prepared for the potential increase in spreads during volatile times.
How Do Spreads Affect Forex Trading Costs?
Spreads are a crucial factor in determining the overall trading costs in Forex. The spread is essentially the broker’s fee for facilitating the trade, directly impacting each trade’s potential profit and loss.

Trading Costs: When a trader opens a position, they must cover the spread cost upfront. For instance, if a trader buys EUR/USD at 1.2000 with a spread of 2 pips, the position will need to move by 2 pips in their favor to break even. This cost can increase, especially for high-frequency traders or those making numerous trades with small profit targets.
Profit and Loss Calculation: The spread affects how quickly a trade can become profitable. A wider spread means the trade must move further in the trader’s favor to achieve profitability. Conversely, a narrower spread allows for quicker realization of profits. Managing spread costs effectively is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and improving overall profitability
What is a Spread’s Influencing Factors?
Several key factors influence the width of spreads in Forex trading, affecting the cost of trading and overall market conditions.
Market Liquidity: The liquidity of a currency pair is one of the most significant factors affecting spreads. Highly liquid pairs, such as EUR/USD or GBP/USD, have tighter spreads due to the high volume of trading activity. In contrast, exotic currency pairs with lower trading volumes generally have wider spreads. Increased liquidity ensures that there are plenty of buyers and sellers, which narrows the spread.
Market Volatility: During periods of high market volatility, such as major economic announcements or geopolitical events, spreads tend to widen. This increase is due to uncertainty and rapid price movements, causing liquidity providers to demand higher spreads to compensate for the additional risk. Conversely, in stable market conditions, spreads are typically narrower.
Time of Day: The time of day also influences spreads. Spreads are generally narrower during the overlap of major trading sessions, such as the London-New York overlap, due to higher trading volumes. During less active periods, such as the Asian session, spreads can widen due to reduced trading activity and liquidity.
Why Do Spreads Vary Between Currency Pairs?
The variation in spreads between different currency pairs can be attributed to several factors:
Currency Pair Liquidity: Major currency pairs, which involve currencies from large, stable economies and are traded in high volumes, typically have tighter spreads. Examples include EUR/USD and USD/JPY. Minor and exotic pairs, which involve less frequently traded currencies, tend to have wider spreads due to lower liquidity and higher volatility. For example, the spread for EUR/USD might be 1-2 pips, while for an exotic pair like USD/TRY, it could be 20-50 pips.
Economic Stability: The economic stability of the countries involved in the currency pair also affects spreads. Pairs involving currencies from stable, developed economies usually have tighter spreads. In contrast, those involving currencies from emerging markets or countries with political instability have wider spreads due to increased risk and lower trading volumes.
How Do Fixed and Variable Spreads Compare?
Forex brokers typically offer two types of spreads: fixed spreads and variable (or floating) spreads.
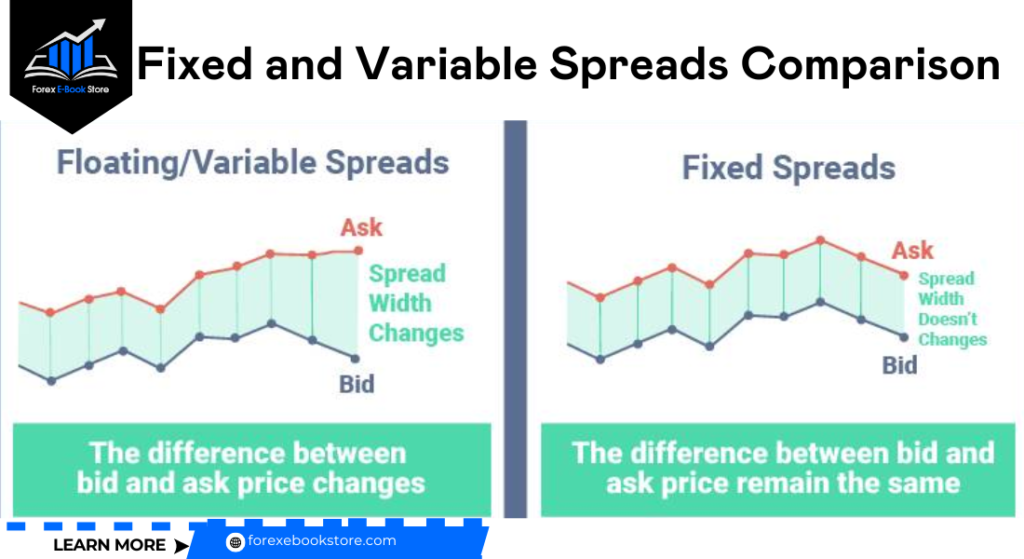
Fixed Spreads: Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. Brokers offering fixed spreads provide stability and predictability for traders, making it easier to calculate trading costs. However, fixed spreads are generally wider than variable spreads to account for the broker’s risk. This type of spread is beneficial for traders who prefer consistency and those who trade during volatile market conditions.
Variable Spreads: Variable spreads fluctuate with market conditions. They tend to be narrower during periods of high liquidity and can widen significantly during volatile market events. Variable spreads offer the potential for lower trading costs during stable market conditions but require traders to be aware of potential widening during high volatility. Experienced traders often prefer variable spreads as they can take advantage of tighter spreads when market conditions are favorable.
How Can Traders Minimize Spread Costs in Forex?
Minimizing spread costs is essential for improving profitability in Forex trading. Here are some effective strategies to help traders reduce these costs:
1. Choose a Reputable Broker: The first step in minimizing spread costs is selecting a broker that offers competitive spreads. Reputable brokers provide tighter spreads due to their larger trading volumes and better access to liquidity providers. It’s important to compare spreads across different brokers and read reviews to ensure reliability and transparency.
2. Trade During Peak Market Hours: Trading during periods of high liquidity, such as when major financial markets overlap (e.g., London and New York sessions), can result in narrower spreads. During these times, the increased trading activity leads to higher liquidity and tighter spreads. Conversely, trading during off-peak hours or when markets are less active can lead to wider spreads due to lower liquidity..
3. Avoid Trading During Major News Releases: Economic news releases and geopolitical events can cause significant market volatility, leading to wider spreads as brokers manage increased risk. Traders can minimize the what is a spread’s costs by avoiding trading during these periods. Monitoring an economic calendar helps traders stay informed about upcoming news events and plan their trades accordingly.
What Role Do Brokers Play in Forex Spreads?
Brokers play a crucial role in determining the spreads that traders encounter in the Forex market. Here are some key aspects of how brokers influence spreads:
1. Market Maker vs. ECN Brokers: Market maker brokers set their bid and ask prices, often leading to fixed spreads. While fixed spreads provide predictability, they may be wider to account for the broker’s risk. On the other hand, ECN (Electronic Communication Network) brokers provide access to multiple liquidity providers, resulting in variable spreads that can be narrower during high liquidity periods. ECN brokers typically charge a commission on trades instead of marking up the spread, which can be more cost-effective for traders.
2. Spread Fluctuations: Brokers adjust spreads based on market conditions, liquidity, and volatility. During periods of high market activity, such as overlapping trading sessions, spreads tend to be narrower. In contrast, during low liquidity or high volatility periods, brokers may widen spreads to mitigate risk. Traders should monitor what is a spread’s fluctuations and choose brokers that offer consistently competitive what is a spreads across different market conditions.
3. Trading Platforms and Tools: Brokers provide various trading platforms and tools that can impact spread costs. Real-time spread monitoring tools and advanced trading platforms enable traders to make informed decisions and take advantage of tighter spreads. Additionally, some brokers offer educational resources and support to help traders understand and manage what is a spreads effectively.
How to Choose the Best Broker Based on Spreads?
Choosing the best broker based on spreads involves considering several factors to ensure competitive pricing and reliable trading conditions:

1. Compare Spreads: Different brokers offer varying spreads for different currency pairs. It’s essential to compare the what is a spreads offered by multiple brokers, focusing on those that provide consistently tight spreads for the currency pairs you trade most frequently. Reputable review sites and broker comparison tools can help in this evaluation.
2. Evaluate the Broker’s Reputation: A broker’s reputation for transparency and reliability is crucial. Look for brokers regulated by reputable financial authorities and read reviews from other traders to gauge their experiences with what is a spread costs and overall service quality. A reliable broker should have a track record of fair pricing and ethical business practices..
3. Consider Account Types and Trading Conditions: Some brokers offer different account types with varying spreads and trading conditions. For example, ECN accounts typically have lower spreads but charge commissions on trades. Understanding the differences between account types and choosing one that aligns with your trading strategy and cost considerations is important. Additionally, ensure the broker provides robust trading platforms and tools to help you manage what is a Spread effectively..
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of a spread in Forex is crucial for traders as it directly impacts the cost of trading. The spread represents the difference between the bid and ask price, influencing the overall profitability of trades. Just like understanding spreads, grasping the meaning of a pip is equally important in Forex trading. A pip measures the smallest price change in a currency pair, and knowing how spreads and pips work together can help traders make more informed decisions and optimize their strategies.
In Forex trading, the spread plays a vital role in determining transaction costs, affecting the potential profits or losses of a trade. By understanding spreads, traders can better manage their positions and expectations. This ties closely with the concept of a pip, which represents the smallest movement in a currency pair’s price. Together, a solid grasp of both spreads and pips allows traders to better navigate the Forex market and enhance their trading accuracy.












