The bid price is a fundamental concept in trading and investing. It represents the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security, asset, commodity, or service at a given time. In financial markets, the bid price is a critical indicator of demand, as it shows the maximum price investors are prepared to offer to acquire a specific asset.
In trading platforms, you will often see the biding price alongside the ask price—the lowest price at which a seller is willing to sell the asset. The difference between these two prices is known as the bid-ask spread, which is a measure of market liquidity and trading costs. Understanding the biding price is essential for making informed trading decisions and effectively managing investments.
Table of Contents
How is the Bid Price Determined?
The bid price is determined by several key factors in the market, primarily revolving around the principles of supply and demand. Here’s a closer look at how these elements interact to set the biding price:
Market Demand and Supply
The biding price is essentially the highest price that a buyer is willing to pay for a security. When there is high demand for a particular asset, multiple buyers might place competitive bids, driving the biding price up. Conversely, if the supply of the asset exceeds demand, the bid price will tend to decrease as buyers are not willing to pay as much for it.
Market Makers and Liquidity
Market makers play a crucial role in determining the biding price. They provide liquidity by being ready to buy (at the bid price) and sell (at the ask price) at any given time. They set these prices based on their assessment of the market conditions, including the current supply and demand dynamics. By maintaining a spread between the biding and ask prices, market makers also ensure they can profit from the difference.
Economic Indicators and Market Sentiment
Economic news and market sentiment significantly impact the bid price. Positive news about an asset or favorable economic indicators can increase demand, pushing up the bid-ask price. Conversely, negative news can reduce demand, causing the biding price to fall. Traders and investors closely monitor these factors to adjust their biding prices accordingly.
Why is the Bid Price Important?
The bid price is a crucial component in trading and investing for several reasons:
Indicator of Market Demand
The bid price reflects the highest amount a buyer is willing to pay for an asset, providing insight into the current market demand. It helps traders and investors gauge the interest in a particular security or asset at any given time.
Basis for Trading Decisions
The biding price, along with the ask price, forms the basis of the bid-ask spread, which is a critical measure of market liquidity. A smaller spread typically indicates higher liquidity and less cost to trade the asset. Traders use this information to make informed decisions about when to enter or exit trades, aiming to minimize costs and maximize profits.
Impact on Transaction Costs
The bid price directly influences the transaction costs for buying and selling securities. For buyers, purchasing at the biding price can mean lower costs, while sellers need to be aware of the bid price to ensure they are getting a fair deal. Understanding the bidimng price helps in negotiating better transaction terms and managing overall trading expenses
What Factors Influence the Bid Price?
The bid price is influenced by various factors that reflect the dynamics of the financial markets. Understanding these factors helps traders and investors make informed decisions.
Market Demand and Supply
The bid price is primarily driven by the supply and demand for a security. When demand is high, buyers are willing to pay more, which increases the bid price. Conversely, if supply exceeds demand, the biding price tends to decrease as buyers are less willing to pay higher prices. This supply-demand balance is fundamental in setting bid prices across different markets.
Market Liquidity
Liquidity, or the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold in the market, also significantly affects the bid price. In highly liquid markets, where trading volumes are high, the bid price tends to be closer to the ask price, resulting in a narrower bid-ask spread. In less liquid markets, the biding price might be much lower than the ask price, leading to a wider spread. This is because fewer buyers and sellers are participating, which increases transaction costs and the risk for market makers.
Economic Indicators and Market Sentiment
Macroeconomic factors such as interest rates, inflation, and GDP growth can influence investor behavior and subsequently the bid price. Positive economic news can boost market sentiment, leading to higher biding prices as buyers are more confident. Conversely, negative economic indicators can reduce demand and lower biding prices. Market sentiment, shaped by geopolitical events, regulatory changes, and overall investor confidence, also plays a crucial role in determining the biding price.
What is the Difference Between Bid Price and Ask Price?
Understanding the difference between bid and ask prices is crucial for anyone involved in trading and investing.
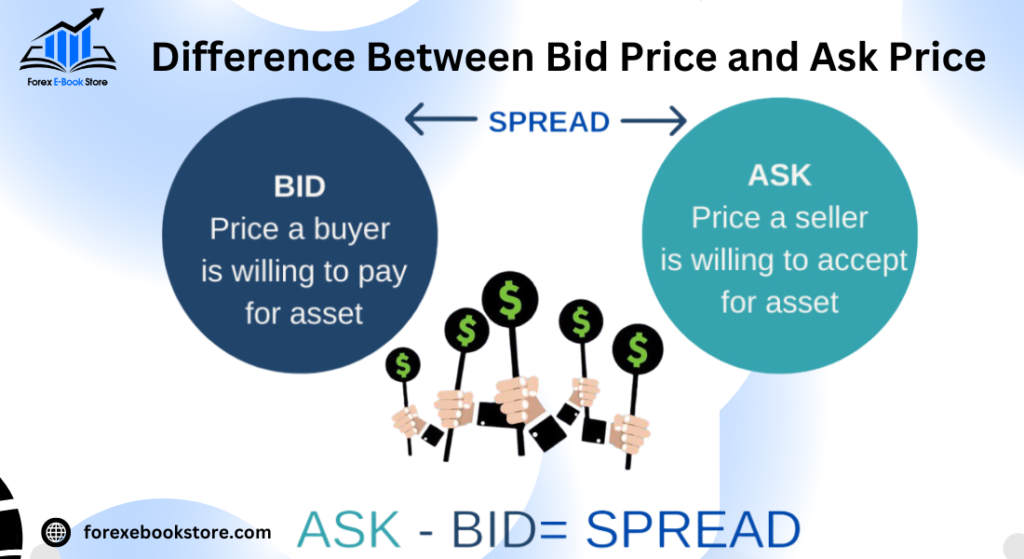
Definition and Role
The bid price is the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security, whereas the ask price (or offer price) is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. Together, these prices form the bid-ask spread, which is a key indicator of market liquidity. The narrower the spread, the more liquid the market is, indicating that the asset can be bought or sold quickly with minimal price impact.
Impact on Transactions
For a transaction to occur, a buyer must agree to the ask price, or a seller must agree to the bid price. The difference between these prices, known as the spread, represents the transaction cost for traders. A smaller spread generally means lower transaction costs and greater market efficiency, which is beneficial for traders looking to minimize costs. Conversely, a larger spread can indicate a less liquid market with higher transaction costs.
How is the Bid-Ask Spread Calculated?
The bid-ask spread is a simple yet essential concept in trading, representing the difference between the bid and ask prices of a security.
Calculation
The bid-ask spread is calculated as the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask price). For example, if the biding price for a stock is $50 and the asking price is $51, the bid-ask spread is $1. This spread indicates the cost of trading the security and is a measure of market liquidity.
Significance
A narrower bid-ask spread typically indicates a highly liquid market, where many buyers and sellers are willing to trade the asset, leading to more efficient pricing. Conversely, a wider spread suggests lower liquidity, higher transaction costs, and potentially greater volatility. Traders and investors monitor the bid-ask spread to gauge the liquidity and trading cost of security, helping them make more informed trading decisions.
Why is the Bid-Ask Spread Significant?
The bid-ask spread is a crucial aspect of trading and investing because it represents the transaction cost for trading an asset. Here’s why it’s significant:
Indicator of Market Liquidity
The bid-ask spread is a direct indicator of market liquidity. A narrow spread typically indicates a highly liquid market where many buyers and sellers are willing to trade the asset, making it easier to enter and exit positions with minimal cost. Conversely, a wider spread suggests lower liquidity, meaning fewer market participants and higher transaction costs.
Impact on Trading Costs
The spread represents a hidden cost in every trade. For example, if you buy a stock at the ask price and sell it at the biding price, the difference (the spread) is the cost you incur. This cost can significantly impact profitability, especially for day traders and high-frequency traders who execute numerous trades daily. Understanding and managing the spread is essential for optimizing trading strategies and minimizing costs.
How Does Liquidity Impact the Bid Price?
Liquidity plays an essential role in determining the bid price and overall market dynamics. Here’s how liquidity impacts the bid price:
Narrower Spreads
High liquidity typically leads to narrower bid-ask spreads. When a market is liquid, there are many buyers and sellers, which increases the chances of matching buy and sell orders quickly. This competition among participants tightens the spread, making it cheaper to trade the asset. For example, highly traded stocks like those of major companies usually have tight spreads due to their high liquidity.
Market Stability
In liquid markets, prices are generally more stable because large trades can be executed without causing significant price changes. This stability is beneficial for traders as it reduces the risk of slippage and ensures that trades are executed close to the expected price. In contrast, in less liquid markets, even small trades can cause large price movements, leading to wider spreads and increased trading costs.
How Do Bid Prices Affect Trading Strategies?
Bid prices are integral to various trading strategies, influencing both the execution and the outcomes of trades. Here’s how they affect trading strategies:

Entry and Exit Points
Traders use bid prices to determine optimal entry and exit points. For example, a trader looking to buy an asset will pay attention to the current biding price to ensure they are getting the best possible price. Similarly, when selling, the ask price becomes crucial. By strategically placing buy and sell orders around these prices, traders can maximize their returns.
Risk Management
Bid prices also play a role in risk management. For instance, traders often set stop-loss orders at certain biding prices to limit potential losses. Understanding the bid-ask dynamics helps traders set these levels more effectively, ensuring they can exit positions with minimal loss during volatile market conditions. Additionally, tight spreads reduce the risk of large, unexpected costs, helping traders manage their overall risk exposure better.
What are Common Mistakes Traders Make with Bid Prices?
Traders often encounter pitfalls when dealing with biding prices, which can significantly impact their trading performance. Here are some common mistakes to avoid:
Ignoring the Bid-Ask Spread
One of the most frequent mistakes is neglecting the bid-ask spread, which represents the transaction cost for trading an asset. Traders who ignore this spread may end up paying higher costs than anticipated, reducing their overall profitability. It’s crucial to consider the spread before executing trades to understand the full cost involved and optimize trade entries and exits.
Trading Based on Emotions
Emotional trading, driven by fear or greed, can lead to poor decision-making. Traders might hold onto losing positions for too long or exit winning trades prematurely due to emotional responses. To avoid this, traders should follow a disciplined trading plan based on objective analysis rather than emotional impulses.
Not Adapting to Market Conditions
Market conditions are dynamic, and the bid-ask spread can widen or narrow based on factors such as volatility and liquidity. Traders who fail to adapt their strategies to these changing conditions may face increased costs and risks. Staying updated on market conditions and adjusting strategies accordingly is essential for successful trading.
How to Use Bid Prices to Make Informed Trading Decisions?
Bid prices provide valuable information that can help traders make more informed decisions. Here’s how to leverage this data effectively:
Monitor Bid-Ask Trends
Regularly monitoring the trends in bid and ask prices can reveal patterns or opportunities in the market. By understanding how these prices fluctuate, traders can better time their trades to maximize profits and minimize costs.
Use Limit Orders
Placing limit orders allows traders to specify the maximum price they are willing to pay or the minimum price they are willing to accept. This helps control the price at which trades are executed, providing more precision and reducing the impact of a fluctuating bid-ask spread.
Evaluate Market Depth
Market depth shows the number of buy and sell orders at various price levels, indicating the level of interest in an asset. Analyzing market depth can help traders gauge potential price movements and make more informed decisions about when to enter or exit positions.
What Tools and Resources Can Help Monitor Bid Prices?
Various tools and resources can aid traders in effectively monitoring and analyzing biding prices:

Trading Platforms
Most trading platforms offer real-time data on bid and ask prices, along with tools to analyze market trends and depth. These platforms provide the necessary information to make timely and informed trading decisions.
Financial News Services
Staying informed about the latest market news and economic indicators can help traders anticipate changes in biding prices. Services like Bloomberg, Reuters, and other financial news providers offer real-time updates and analyses that are crucial for trading decisions.
Analytical Tools
Using analytical tools such as charting software and market scanners can help traders visualize trends and identify patterns in bid and ask prices. These tools often include features like technical indicators and historical data analysis, which are invaluable for developing and refining trading strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the ask price is essential for forex traders as it represents the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a currency. This price is crucial for buying decisions and impacts the overall cost of a trade. Additionally, it is important to recognize the interplay between the ask price and the bid price—the highest price a buyer is willing to pay. The difference between these two prices, known as the spread, can significantly influence trading strategies and profitability. To gain a comprehensive view of forex trading dynamics, it’s beneficial to also explore our article on “What is the Ask Price?” which delves into the other side of the transaction and its implications on market activities. Understanding both ask and bid prices equips traders with the knowledge needed to navigate the forex market effectively.










